7.2.8 – Packet Tracer – Verify IPv4 and IPv6 Addressing
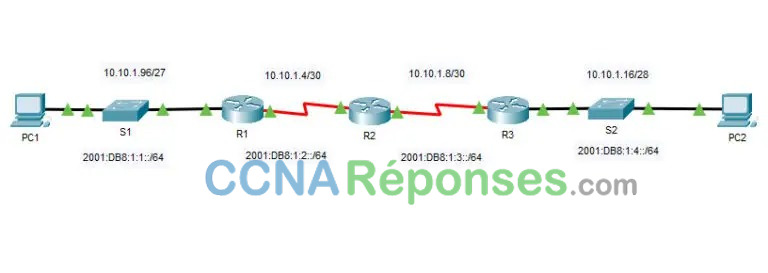
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address / Prefix | Default Gateway | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0 | 10.10.1.97 | 255.255.255.224 | N/A |
| 2001:db8:1:1::1/64 | ||||
| S0/0/1 | 10.10.1.6 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| 2001:db8:1:2::2/64 | ||||
| fe80::1 | ||||
| R2 | S0/0/0 | 10.10.1.5 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A |
| 2001:db8:1:2::1/64 | ||||
| S0/0/1 | 10.10.1.9 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| 2001:db8:1:3::1/64 | ||||
| fe80::2 | ||||
| R3 | G0/0 | 10.10.1.17 | 255.255.255.240 | N/A |
| 2001:db8:1:4::1/64 | ||||
| S0/0/1 | 10.10.1.10 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| 2001:db8:1:3::2/64 | ||||
| fe80::3 | ||||
| PC1 | NIC | 10.10.1.100 | 255.255.255.224 | 10.10.1.97 |
| 2001:db8:1:1::a/64 | fe80::1 | |||
| PC2 | NIC | 10.10.1.20 | 255.255.255.240 | 10.10.1.17 |
| 2001:db8:1:4::a/64 | fe80::3 | |||
Objectives
Part 1: Complete the Addressing Table Documentation
Part 2: Test Connectivity Using Ping
Part 3: Discover the Path by Tracing the Route
Background
Dual-stack allows IPv4 and IPv6 to coexist on the same network. In this activity, you will investigate a dual-stack implementation including documenting the IPv4 and IPv6 configuration for end devices, testing connectivity for both IPv4 and IPv6 using ping, and tracing the path from end to end for IPv4 and IPv6.
Instructions
Part 1: Complete the Addressing Table Documentation
Step 1: Use ipconfig to verify IPv4 addressing.
a. Click PC1 and open the Command Prompt.
b. Enter the ipconfig /all command to collect the IPv4 information. Fill-in the Addressing Table with the IPv4 address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
c. Click PC2 and open the Command Prompt.
d. Enter the ipconfig /all command to collect the IPv4 information. Fill-in the Addressing Table with the IPv4 address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
Step 2: Use ipv6config to verify IPv6 addressing.
a. On PC1, enter the ipv6config /all command to collect the IPv6 information. Fill-in the Addressing Table with the IPv6 address, subnet prefix, and default gateway.
b. On PC2, enter the ipv6config /all command to collect the IPv6 information. Fill-in the Addressing Table with the IPv6 address, subnet prefix, and default gateway.
Part 2: Test Connectivity Using Ping
Step 1: Use ping to verify IPv4 connectivity.
a. From PC1, ping the IPv4 address for PC2.
Was the result successful?
Oui
b. From PC2, ping the IPv4 address for PC1.
Was the result successful?
Oui
Step 2: Use ping to verify IPv6 connectivity.
a. From PC1, ping the IPv6 address for PC2.
Was the result successful?
Oui
b. From PC2, ping the IPv6 address of PC1.
Was the result successful?
Oui
Part 3: Discover the Path by Tracing the Route
Step 1: Use tracert to discover the IPv4 path.
a. From PC1, trace the route to PC2.
PC> tracert 10.10.1.20
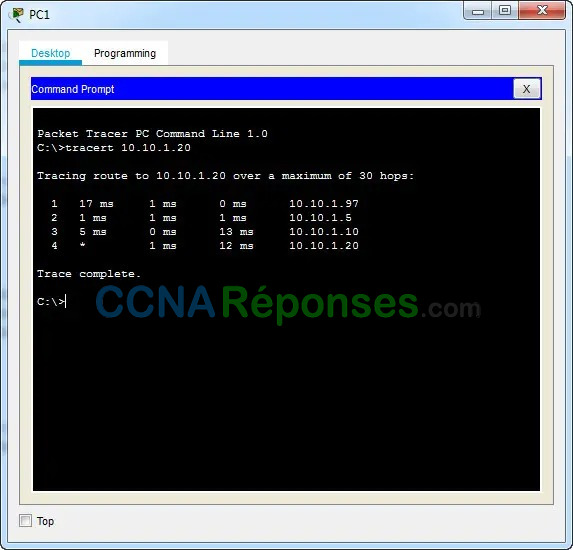
What addresses were encountered along the path?
10.10.1.97, 10.10.1.5, 10.10.1.10, 10.10.1.20
With which interfaces are the four addresses associated
G0/0 of R1, S0/0/0 on R2, S0/0/01 on R3, NIC of PC2
b. From PC2, trace the route to PC1.
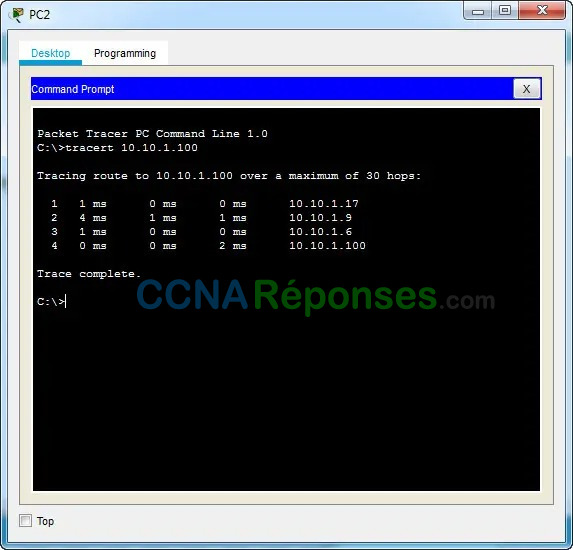
What addresses were encountered along the path?
10.10.1.17, 10.10.1.9, 10.10.1.6, 10.10.1.100
With which interfaces are the four addresses associated?
G0/0 of R3, S0/0/1 of R2, S0/0/1 of R1, NIC of PC1
Step 2: Use tracert to discover the IPv6 path.
a. From PC1, trace the route to the IPv6 address for PC2.
PC> tracert 2001:db8:1:4::a
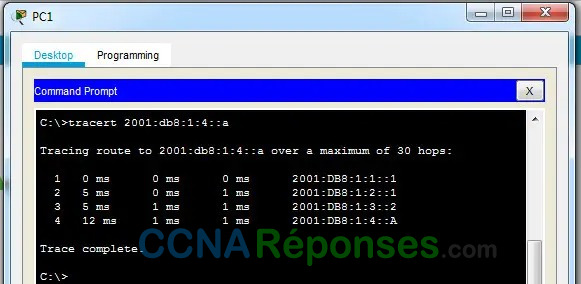
What addresses were encountered along the path?
2001:db8:1:1::1, 2001:db8:1:2::1, 2001:db8:1:3::2, 2001:db8:1:4::a
With which interfaces are the four addresses associated?
G0/0 of R1, S0/0/0 of r2, S0/0/1 of R3, NIC of PC2
b. From PC2, trace the route to the IPv6 address for PC1.
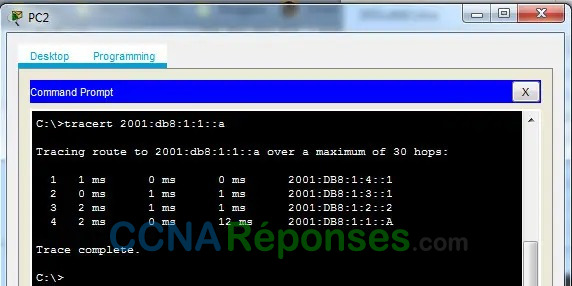
What addresses were encountered along the path?
2001:db8:1:4::1, 2001:db8:1:3::1, 2001:db8:1:2::2, 2001:db8:1:1::a
With which interfaces are the four addresses associated?
G0/0 of R3, S0/0/1 of R2, S0/0/1 of R1, NIC of PC1
